لماذا تُعدّ مقاومة فيلم حماية الصفائح (PPF) لدرجات الحرارة العالية والمنخفضة مهمة؟
تتعرض السيارات لنطاق واسع من درجات الحرارة على مدار العام، وقد تؤثر هذه الظروف القاسية سلبًا على الطلاء غير المحمي وحتى على طبقات الحماية الشفافة منخفضة الجودة. إليكم سبب كون ثبات درجة الحرارة عاملًا حاسمًا في أداء طبقات الحماية الشفافة:
-
منع تدهور الموادقد تؤدي درجات الحرارة المنخفضة إلى جعل طبقة الحماية الشفافة هشة، مما يتسبب في تشققها أو تقشرها أو فقدانها للالتصاق. أما درجات الحرارة المرتفعة، فقد تتسبب في انحناء الطبقة أو تغير لونها (اصفرارها) أو فقدانها لصلابة طبقتها الواقية.
-
الحفاظ على الوظيفة الوقائيةتتمثل الوظيفة الأساسية لطبقة الحماية الشفافة (PPF) في الحماية من الخدوش، وتلفيات الحصى، والأشعة فوق البنفسجية، والملوثات الكيميائية. ويمكن أن تؤثر درجات الحرارة القصوى سلبًا على هذه الوظائف؛ فعلى سبيل المثال، لن تمتص الطبقة الهشة في الطقس البارد الصدمات جيدًا، بينما تكون الطبقة اللينة في الطقس الحار أكثر عرضة للخدوش.
-
متانة طويلة الأمدتدوم طبقة الحماية الشفافة (PPF) التي تتحمل درجات حرارة تتراوح بين -30 درجة مئوية و80 درجة مئوية لفترة أطول، موفرةً حماية مستمرة لمدة تتراوح بين 5 و10 سنوات (بحسب الجودة). أما الطبقات ذات المقاومة المنخفضة للحرارة فتؤدي إلى تلفها المبكر، مما يستدعي إعادة تطبيقها بتكلفة باهظة.
-
قابلية التطبيق العالميةسواء كنت تعيش في منطقة ذات شتاء قاسٍ (مثل كندا، الدول الاسكندنافية) أو صيف حار (مثل الشرق الأوسط، أريزونا)، فإن طبقة الحماية من الرصاص المستقرة حرارياً تضمن حماية موثوقة بغض النظر عن المناخ.
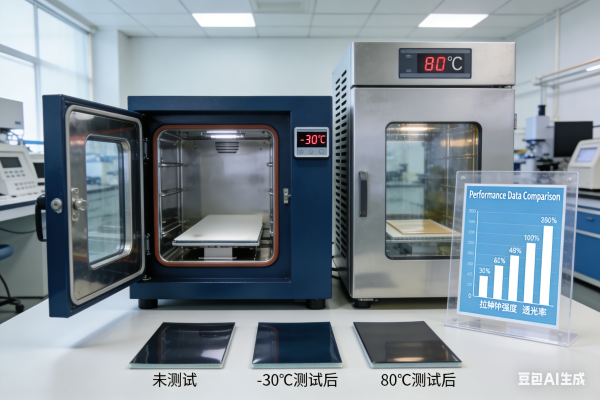
اختبار مقاومة PPF لدرجات الحرارة العالية والمنخفضة: من -30 درجة مئوية إلى 80 درجة مئوية. معايير وعملية الاختبار
لتقييم استقرار مادة PPF في الظروف البيئية بين -30 درجة مئوية و80 درجة مئوية، تُجرى اختبارات احترافية وفقًا لمعايير صناعية صارمة (مثل ASTM D1598 لمرونة درجات الحرارة المنخفضة وASTM D4329 للتقادم الحراري). فيما يلي شرح مفصل لعملية الاختبار:
1. تحضير عينة الاختبار
تُقطع عينات الاختبار من لفة غشاء البولي بروبيلين الشفاف (عادةً 100 مم × 200 مم) لضمان التناسق. تشمل العينات كلاً من الغشاء نفسه وطبقة المادة اللاصقة، حيث يُعدّ الالتصاق عاملاً حاسماً للأداء في درجات الحرارة القصوى. تُحضّر عينات متعددة لاختبار معايير مختلفة (المرونة، الالتصاق، تغير اللون).
2. اختبار مقاومة درجات الحرارة المنخفضة (-30 درجة مئوية)
يركز اختبار درجة الحرارة المنخفضة على مرونة الفيلم وقوة التصاقه لمنع التشقق والتقشر في ظروف التجمد:
-
يتم وضع العينات في غرفة يتم التحكم في مناخها عند درجة حرارة -30 درجة مئوية ويتم الاحتفاظ بها لمدة 24-48 ساعة (محاكاة التعرض للبرد على المدى الطويل).
-
بعد المعالجة، يتم إزالة العينة وإخضاعها على الفور لاختبار المرونة: حيث يتم ثنيها حول مندريل (أداة أسطوانية) بأقطار مختلفة (من 10 مم إلى 50 مم) للتحقق من وجود تشققات أو تمزقات.
-
اختبار الالتصاق: تُوضع العينة المُعالجة على لوحة طلاء سيارات قياسية، ويُجرى اختبار تقشير (باستخدام جهاز اختبار الشد) لقياس القوة اللازمة لتقشير الفيلم من اللوحة. يجب أن يحتفظ فيلم حماية الطلاء عالي الجودة بنسبة ≥90% من قوة التصاقه الأصلية عند درجة حرارة -30 درجة مئوية.
![]()
3. اختبار مقاومة درجات الحرارة العالية (80 درجة مئوية)
يقيّم اختبار درجة الحرارة العالية التقادم الحراري وتغير اللون والاستقرار الأبعاد - وهي عوامل رئيسية للأداء الصيفي:
-
يتم وضع العينات في غرفة تقادم حراري عند درجة حرارة 80 درجة مئوية لمدة 72-168 ساعة (محاكاة التعرض المطول لأشعة الشمس ودرجات الحرارة المحيطة العالية).
-
بعد المعالجة الحرارية، يتم فحص العينة بحثًا عن تغير اللون باستخدام مقياس الألوان (قياس قيمة ΔE؛ تعتبر قيمة ΔE < 1 ممتازة، مما يشير إلى الحد الأدنى من الاصفرار).
-
اختبار ثبات الأبعاد: يُقاس طول وعرض العينة قبل وبعد تعريضها للحرارة. يجب أن يكون التغير في أبعاد مادة البولي بروبيلين عالية الجودة ≤ 1% (مما يمنع التشوّه أو الانكماش).
-
اختبار الصلابة: تُقاس صلابة الطبقة العلوية للفيلم باستخدام اختبار صلابة القلم الرصاص (ASTM D3363). يجب أن يحتفظ فيلم الحماية الشفاف الجيد بصلابة ≥H بعد التعرض للحرارة، مما يضمن مقاومته للخدوش.
4. اختبار درجة الحرارة الدورية (-30 درجة مئوية إلى 80 درجة مئوية)
لمحاكاة ظروف العالم الحقيقي (حيث تتقلب درجات الحرارة بين النهار والليل أو من موسم لآخر)، يتم إجراء اختبار دوري:
-
يتم تعريض العينات لدورات متناوبة من -30 درجة مئوية (12 ساعة) و80 درجة مئوية (12 ساعة) لمدة 10-20 دورة.
-
بعد دورات التشغيل، تُختبر العينات للتأكد من قوة الالتصاق، والمرونة، وعدم تغير اللون، والسلامة الهيكلية. يجب ألا يُظهر غشاء الحماية من التلف (PPF) الذي يجتاز الاختبار أي تشققات أو تقشر أو فقدان ملحوظ في الأداء.
نتائج الاختبار الرئيسية: ما الذي يجعل طبقة الحماية من الرصاص عالية الجودة عند درجات حرارة تتراوح من -30 درجة مئوية إلى 80 درجة مئوية؟
بعد إجراء اختبارات صارمة، ستفي أغشية البولي بروبيلين عالية الجودة التي تتفوق في استقرارها البيئي من -30 درجة مئوية إلى 80 درجة مئوية بالمعايير التالية:
-
أداء في درجات الحرارة المنخفضة (-30 درجة مئوية): لا يوجد تشقق أو تمزق أثناء اختبار المرونة؛ الاحتفاظ بالالتصاق ≥90%؛ يبقى مرنًا بما يكفي ليتوافق مع منحنيات السيارة دون تقشير.
-
أداء عالي الحرارة (80 درجة مئوية): تغير طفيف في اللون (ΔE < 1)؛ تغيير الأبعاد ≤1%؛ صلابة الطبقة العلوية ≥H؛ لا يوجد تشوه أو تليين يؤثر على مقاومة الخدش.
-
أداء الاختبار الدوري: يحافظ على جميع الخصائص الأساسية (الالتصاق، المرونة، الصلابة) بعد أكثر من 10 دورات حرارية؛ لا يوجد ضرر مرئي (تشققات، تقشير، اصفرار).
ملاحظة: غالبًا ما تفشل أفلام الحماية من التلف (PPF) منخفضة الجودة في هذه الاختبارات، فقد تتشقق عند درجة حرارة -30 درجة مئوية، أو تصفر بشدة عند 80 درجة مئوية، أو تتقشر بعد عدة دورات حرارية. لذا، اطلب دائمًا تقرير اختبار من الشركة المصنعة قبل شراء أفلام الحماية من التلف.
كيفية اختيار مادة PPF المناسبة لدرجات الحرارة القصوى (-30 درجة مئوية إلى 80 درجة مئوية)؟
استنادًا إلى نتائج الاختبارات والأداء في العالم الحقيقي، إليك 5 نصائح لاختيار واقي الشمس المناسب لدرجات الحرارة القصوى:
1. تحقق من شهادات اختبار الشركة المصنعة
توفر العلامات التجارية الموثوقة لأغشية الحماية من الرصاص (مثل XPEL و3M وSunTek) تقارير اختبار مفصلة لمقاومة درجات الحرارة العالية والمنخفضة. ابحث عن التقارير التي تختبر تحديدًا نطاق درجات الحرارة من -30 درجة مئوية إلى 80 درجة مئوية، وتؤكد الامتثال لمعايير الصناعة (ASTM D1598 وASTM D4329).
2. إعطاء الأولوية للمواد اللاصقة والطبقة النهائية عالية الجودة
تُعدّ الطبقة اللاصقة أساسيةً للالتصاق في درجات الحرارة المنخفضة، لذا يُنصح باختيار طلاء PPF ذي لاصق أكريليكي أو بولي يوريثان (يقاوم التكسر في البرد). أما الطبقة العلوية، فينبغي أن تكون شديدة اللمعان ومقاومة للأشعة فوق البنفسجية (تمنع الاصفرار في الحرارة) وبصلابة ≥H.
3. تجنب استخدام مواد حماية الطلاء الرخيصة وغير المعروفة العلامة التجارية
تستخدم أفلام الحماية الرخيصة مواد رديئة الجودة تتلف في درجات الحرارة القصوى. قد توفر لك المال في البداية، لكنها ستحتاج إلى استبدالها بعد سنة أو سنتين، مما يكلفك أكثر على المدى الطويل.
4. مراعاة الاحتياجات الخاصة بالمناخ
إذا كنت تعيش في منطقة ذات برودة شديدة (مثلاً، تصل درجة الحرارة إلى -30 درجة مئوية بانتظام)، فاحرص على اختيار ملابس واقية من الرصاص تتميز بمرونة عالية في درجات الحرارة المنخفضة. أما إذا كنت تعيش في مناخ حار (مثلاً، تصل درجة الحرارة في الصيف إلى 80 درجة مئوية)، فركز على الملابس المقاومة للحرارة والحماية من الأشعة فوق البنفسجية.
5. اختر خدمة التركيب الاحترافية
حتى أفضل أنواع أفلام الحماية من التلف (PPF) ستفشل إذا تم تركيبها بشكل سيئ. يستخدم الفنيون المحترفون الأدوات والتقنيات المناسبة لضمان التصاق الفيلم بشكل متساوٍ، مما يمنع ظهور فقاعات الهواء أو التقشير الذي قد يتفاقم في درجات الحرارة القصوى.
أسئلة شائعة حول مقاومة فيلم الحماية من التسرب (PPF) لدرجات الحرارة العالية والمنخفضة
س1: هل يتحمل فيلم الحماية من التجمد درجة حرارة -30 درجة مئوية؟ هل سيتشقق في الطقس المتجمد؟
لن يتشقق غشاء الحماية من التجمد عالي الجودة (المختبر حتى -30 درجة مئوية). ويحافظ على مرونته بفضل جودة غشائه ومواده اللاصقة الممتازة. أما غشاء الحماية من التجمد منخفض الجودة، فقد يصبح هشًا ويتشقق.
س2: هل سيصفر طلاء الحماية من الصبغة عند درجة حرارة 80 درجة مئوية؟
تتميز طبقات الحماية من الأشعة فوق البنفسجية عالية الجودة بطبقة علوية مقاومة للأشعة فوق البنفسجية، مما يقلل من اصفرارها (ΔE < 1) عند درجة حرارة 80 درجة مئوية. أما طبقات الحماية الرخيصة فتفتقر إلى الحماية الكافية من الأشعة فوق البنفسجية، وتصفر بشدة عند درجات الحرارة المرتفعة.
س3: ما هي مدة بقاء PPF في درجات الحرارة القصوى (-30 درجة مئوية إلى 80 درجة مئوية)؟
تدوم طبقة الحماية من الرصاص عالية الجودة، التي تجتاز اختبارات الثبات في درجات حرارة تتراوح بين -30 درجة مئوية و80 درجة مئوية، من 5 إلى 10 سنوات في الظروف المناخية القاسية. ويمكن إطالة عمرها من خلال الصيانة الدورية (الغسل بصابون لطيف، وتجنب المواد الكيميائية القاسية).
س4: هل اختبار درجة الحرارة الدورية مهم لـ PPF؟
نعم! تحاكي الاختبارات الدورية تقلبات درجات الحرارة في العالم الحقيقي (مثل الليل والنهار، الشتاء والصيف). يُعد غشاء الحماية الشفاف (PPF) الذي يُظهر أداءً جيدًا في الاختبارات الدورية أكثر موثوقية من الغشاء الذي يجتاز فقط اختبارات درجات الحرارة العالية أو المنخفضة الثابتة.
الخلاصة: استثمر في طلاء حماية من الخدوش والبقع المقاومة للحرارة لحماية طويلة الأمد
تُعدّ درجات الحرارة القصوى (من -30 درجة مئوية إلى 80 درجة مئوية) اختبارًا رئيسيًا لأغشية حماية الطلاء، ولا يُمكن توفير حماية طويلة الأمد لطلاء سيارتك إلا باستخدام أغشية عالية الجودة ومستقرة حراريًا. من خلال فهم عملية اختبار مقاومة درجات الحرارة العالية والمنخفضة، والنتائج الرئيسية، ونصائح الاختيار، يُمكنك اتخاذ قرار مدروس وتجنب الأخطاء المكلفة.
تذكر: اختر دائمًا طبقة حماية الطلاء (PPF) ذات مقاومة معتمدة للحرارة، واحرص على استخدام مواد عالية الجودة، واستعن بفني متخصص للتركيب. مع طبقة الحماية المناسبة، سيبقى طلاء سيارتك محميًا، سواء كان الجو باردًا جدًا أو حارًا جدًا.
هل تبحث عن مزيد من المعلومات حول اختبار طبقة الحماية الشفافة أو توصيات المنتجات؟ تواصل مع فريق خبراء حماية السيارات لدينا اليوم!


